- Used for creating web applications using spring.
- M stands for model, V stands for view, and C stands for controller
- Model is used to hold data.
- View is used for presentation of data.
- Controller is used for processing data where our business logic is written.
- It implements all the basic features of a core spring framework like inversion of control, dependency injection.
- A spring MVC is sub framework of spring framework. It is used to build web applications.
- It is built on top of servlet API.
- It follows the model view, controller design pattern.
- Spring MVC separates Model, view and controller layers, thus avoiding spaghetti code.
- Power configuration for application using spring configuration options.
- Rapid application development.
- Spring MVC is flexible, easy to test and has much features.
- Spring MVC helps us to organise code in our applications that improving its maintainability and scalability.
- Spring MVC works on Client server architecture.
- Features of Spring Framework
- Supports POJO over EJB.
- Dependency injection
- MVC
- REST
- Security
- Batch
- Data
- AOP
- Can integrate with Hibernate and Struts.
- Client sends request to the front controller, which uses handler mapping to delegate a request to Controller.
- The controller then handles the request using different services and sends response back to front controller.
- The response includes model which contains process, data and view which will be used to render response.
- The front controller then with The help of view resolver fits data in the view. Our static page is added with dynamic data.
- The front controller, then sends back this response to the client.
- Front controller is also a servlet in spring MVC.
- It is called as Dispatcher Servlet.
- The Dispatcher Servlet decides which controller to call for a request.
- Dispatcher servlet has a configuration file which defines which request should be handled by which controller.
- This configuration can also be done by annotations.
- The client only interacts with the front and controller.
- All the request go to the Dispatcher Servlet via web.xml which is the front controller.
- We define our dispatcher servlet in web.xml file along with path to its configuration file.
- In the configuration of dispatcher servlet we add Web MVC Configuration
- Controllers are separated from view so that it allows separation of concerns
- All controllers are annotated with @Controller.
- We have multi action controllers
- The front controller is provided by spring MVC itself.
- Allows separation of concerns that is all modules are separated
- Sending data from controller to view
- We use following classes to send data from controller to view
- Model
- Use method addAttribute(String key,Object value)
- ModelAndView
- Use method addObject(String key,Object Value)
- Sending data from view to controller.
- We send data from JSP page to controller.
- We use HTML form in view to send data back to controller using HTTP post method using forms.
- We add the URL in action property of form element to which we want to send data.
- We can then add a button element with type as submit which submit the data using different elements such as
- Text field
- Check box
- Radio button
- Button
- We can also send via URL in back end.
- We can Use query parameters to send data in backend.
- All this data is added to a model.
- We can get the data from object using getParameter(“name of field”) Which is the method of HttpServletRequest class.
- We are passing the name of the field as a parameter.
- We can also get field values from @RequestParam Annotation in controller function parameters.
- We add this annotation before the parameter name.
- If we want to get all the fields in one object, we use @ModelAttribute
- For this, we must create a class which has all the parameters sent by the form.
- The attributes are then automatically mapped to the object of the class
- We get the data added in the model in HttpServletRequest class object.
- Use method request.getAttribute(“key”).
- @Component Annotations
- @Controller annotation is part of @Component annotation.
- @Repository annotation is part of @Component annotation.
- @Service annotation is part of @Component annotation.
- @Configuration is used to provide dispatcher servlet configuration.
- @Bean is used to create beans.
- @RequestMappingAnnotation
- Used to map URL to handlers
- We can use it above method or above classes
- When we use above classes, the entire controller is mapped to the handler so we must add the prefix to the URL.
- Types of properties inside this annotation are as follows
- Path
- Method
- For type of request.
- @RequestParamAnnotation
- Used to fetch request parameters.
- @ModelAttribute annotation
- Automatically Maps data from view to the object.
- The object should have same attributes or properties as sent by the view.
- We use this annotation in parameters of handler or above method.
- When we add above method, all the properties in the method are added automatically by default to the model.
- Thus we do not need to add common properties to model in each and every handler.
- When we add in parameter of handler, it automatically gets mapped from request and gets added in the model.
- @PathVariable Annotation
- @PathVariable annotation is used to bind method parameter to URI template variable.
- It takes mapping from @RequestMapping.
- URL example @RequestMapping(“/book/{id}”)
- Public String handler(@PathVariable(“id”) int id) {}
- Configuring spring MVC with spring ORM.
- We use an architecture as follows
- Our controller calls, service layer or service class.
- The service class calls, database layer or user DAO
- The database layer calls DB.
- File uploading in spring MVC
- We can upload using Ajax or server side Using spring MVC libraries.
- We upload using MultiPartResolver.
- Resolves data coming from client.
- We need to include commons.io Library and common file upload library.
- Exception handling in spring MVC
- We can have controller based exception, handling or global exception handling.
- In global exception handling, we use @ControllerAdvice annotation above class.
- We annotate the methods with @ExceptionHandler and @ResponseStatus annotation as follows.
@ControllerAdvice public class MyExceptionHandler { @ResponseStatus(value=HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR) @ExceptionHandler({NullPointerException.class}) public String NullExceptionHandler(Model m) { System.out.println("Centralized Null Pointer Exception Occurred"); m.addAttribute("msg","Centralized Null Pointer Exception"); return "null_error"; } @ResponseStatus(value=HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR) @ExceptionHandler({ConversionException.class,NumberFormatException.class}) public String ConversionExceptionHandler(Model m) { System.out.println("Centralized Number Format Exception Occurred"); m.addAttribute("msg","Centralized Number Format Exception"); return "null_error"; } @ResponseStatus(value=HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR) @ExceptionHandler({Exception.class}) public String GenericExceptionHandler(Model m) { System.out.println("Centralized General Exception Occurred"); m.addAttribute("msg","Centralized General Exception"); return "null_error"; } }- If we place the above methods in a class annotated with @GlobalAdvice They become global else if we place them in @Controller they become local to that controller.
- Spring MVC interceptor
- Spring interceptor is a mediator which gets involved before and after our code.
- Spring interceptor is used to intercept client request.
- It is used when we want to modify request and response body.
- We extend handlerinterceptor Class to create an interceptor.
- We implement webmvcconfigure Interface to register an interceptor
- Helps us to do processing before handler, after handler And after view has rendered.
- We use handler interceptor interface to create an Interceptor.
- We can also extend class HandlerInterceptorAdapter To create an interceptor.
- We can also set interceptors in request template setInterceptors method.
- We need to override following 3 methods
- preHandler Returns Boolean
- Prehandle is invoked before a handle invokes.
- If return is true It looks for next interceptor or handler to run.
- If return is false, it sends back response from current interceptor.
- postHandle returns void
- Post handle runs after handler has run.
- afterCompletion returns void.
- After completion runs after view is rendered.
- If there is some exception in the controller, then Post handle will not run, but after completion, will run.
- One way to bind interceptor to a URL Is using WebMvc configurer Interface in the addInterceptor method.
- Another way is using Custom Annotation.
- We can use point cut and advice of aspect oriented programming for invoking interceptor at annotation.
- Example
- https://github.com/gauravmatta/springmvc/blob/283afb88e29e68a696a1066e403f03c5f6ae36ca/voting-system/src/main/java/com/springimplant/votingsystem/interceptor/VotingInterceptor.java
- https://github.com/gauravmatta/springmvc/blob/283afb88e29e68a696a1066e403f03c5f6ae36ca/voting-system/src/main/java/com/springimplant/votingsystem/config/InterceptorConfig.java
- Spring MVC Validators
- We use @interface To create an validator constraint.
- There are some default validators Also given by spring boot, start a validation dependency
- @Not Blank
- @Not Null
- @JsonFormat(pattern=“dd-mm-yyyy”)
- We use @Constraint(validatedBy=“Implementor Validator Class”)
- Validator class provide, constraint Validator Logic.
- Validator class Implements, ConstraintValidator.
- Example
- Spring MVC Resolver
- Resolve interfaces helps us configure our application aspects at global level
- There are following types of resolvers in spring
- View Resolver
- View resolver segregates view configuration from remaining application.
- Makes view, configuration, loosely, coupled.
- Exception Handler Resolver
- Redirection in spring MVC
- We can redirect in three ways
- Redirect Prefix
@RequestMapping("/one") public String one() { System.out.println("This is one Handler"); return "redirect:/enjoy"; }- Redirect View
@RequestMapping("/two") public RedirectView two() { System.out.println("This is two Handler"); RedirectView redirectView = new RedirectView(); redirectView.setUrl("enjoy"); return redirectView; }- HttpServletResponse
- Setup a spring MVC project.
- Building basic foundation of our project.
- Pull in different libraries we need for Spring MVC Project through Maven.
- Configure logging.
- Setup directory structure.
- Apply project facets.
- Project template or Project shell of a Spring MVC project.
- Configure the Dispatcher servlet in web.xml
- Create spring configuration file.
- Configure view resolver.
- Create controller.
- Create view to show page.
- Configure the dispatcher servlet.
- How it performs Request processing.
- Different beans in Dispatcher servlet that we must configure in order to perform request processing through our controllers and in order to display our views.
- These beans are put in place and we have a basic MVC application.
- Application uses XML configurations which are backbones of Spring MVC application.
- Layers in a Spring MVC Application
- Configuration
- Controller
- DAO
- Model
- Services
- Spring MVC projects are setup on Maven.
- So its a good idea to start building them from scratch.
- Maven has a good dependency resolution feature.
- Maven is a built management tool.
- Allows us to manage libraries in a Spring MVC application.
Creating a Maven Project
- Open a new project dialog.
- Search and select Maven Project.
- Check the box "create a simple project".
- Click next button.
- Add a groupId : com.springimplant.mvc
- Add an artifactId : course-project.
- GroupId and ArtifactId are like an address in Maven.
- Click Finish and STS will load a new project.
- This is a java standalone project configured as a Maven Project.
- We need to change this to a web project.
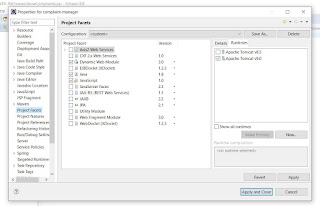
- We use a project facet
- Facet defines characteristics of a project that must be in place when we run the project.
- Right click on project
- Scroll to Configure option
- Select Convert to faceted form.
- Select "Dynamic Web Module" from Project Facets and change its version to 3.1 so that we have support for latest version of servlet API.
- Make sure JRE system library version in Java Build Path matches the version of java in Project facets.
- Next in Java Build Path we will add server runtime for our Application server.This will add the implementation of the servlet API from our server.
- This resolves any sort of import issues with a http servlet request or http servlet response or a http servlet.
- Helps to resolve errors like class "javax.servlet.javax.servlet.HttpServlet" not found during deployment.
- An application server such as Tomcat must be pre configured in your IDE for this.
- This can be either added from the Java Build Path as follows in eclipse
- Or From Project Facets as follows in eclipse
- Once these configurations are done click ok
- We have certain new things
- A TC server
- A new runtime.
- A new folder called as Web Content.
- This was added because we converted to a web project or a dynamic web module facet.
- Delete folder "Web Content" because it is not in alignment with Maven Standard Directory layout.
- Add a new folder under src=>main called as webapp to comply with Maven Standard Directory.
- We need to specify this folder for our Deployment part.
- Open project properties
- Select "Deployment Assembly".
- Select folder
- Next and select the webapp folder click ok.
- In this folder add a new jsp file called as home.jsp
- Type something in the body
- Now we need to set our web.xml file
- We don't have the WEB-INF directory underneath webapp directory.
- Right click on project select Java EE tools.
- Select generate deployment descriptor stub.
- Now we have the WEB-INF directory and with in the directory we have the web.xml file.
- We have a standards compliant Maven's application that is configured with an eclipse dynamic web project facet which make it a web project.
- We have a web.xml and home.jsp file
- To test click on home.jsp file select run as menu and select run on server.
- Select the server
- Server starts and you will see page in browser.
- We have a web project till now.
- Now we will configure spring MVC framework in the same.
- We will use Maven to help us resolve dependencies in our project.
- Open pom.xml file and go to dependencies tab.
- Click on Add.
- Search for "org.springframework".
- select "spring-webmvc" artifact and save the file.
- In dependency hierarchy tab you will see that all the dependencies are automatically loaded by Maven.
- We will add logging dependencies now and we will use slf4j for logging.
- We will add slf4j which is a logging facade.
- Since it is a logging facade we will need an implementation for it as well.
- Click to add dependency.
- Search "slf4j-log4j" artifact.
- Select "slf4j-log4j13" and click ok.
- Click add again to add implementation
- Search for log4j.
- Select log4j and click ok.
- This artifact is identified by default as a "bundle".
- Select properties and change type from "bundle" to "jar".
- Now we need to provide a configuration file for log4j.
- Under source=>main=>resources
- Add a new file called as log4j.properties.
- Add log4j configuration in the same
# Define the root logger with appender X
log4j.rootLogger = DEBUG, stdout
#Direct log messages to stdout
log4j.appender.stdout=org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender
log4j.appender.stdout.Target=System.out
log4j.appender.stdout.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.stdout.layout.conversionPattern=%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss} %-5p %c{1}:%L - %m%n
Configuring Dispatcher Servlet
- The dispatcher servlet is Spring MVC's central servlet that dispatches requests to controller within our application.
- This servlet is also integrated in our Spring IOC container.
- This allows you to configure dispatcher servlet along side other Spring projects and beans.
- Go to src=>main=>webapp=>WEB-INF=>web.xml
- Remove <welcome-file-list> tag and its children.
- Next we will configure our dispatcher servlet.
- This is a regular servlet which extends the http servlet base class.
- Add the tags as shown in file starting with servlet tag which has two sub tags.
- "servlet-name" will contain servlet name.
- "servlet-name" points to dispatcher servlet.
- "servlet-class" contains servlet class.
- "servlet-class" points to "org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet".
- Set "load-on-startup" to 1.
- This tells our application that this will be the first servlet to load when our application starts.
- This ends the "servlet" tag.
- Next we have the "servlet-mapping" tag with following children.
- In this tag we have the "servlet-name" will be dispatcher.
- The "url-pattern" tag in this will be "/".
- This url pattern will be handled by servlet.
- This ends the "servlet-mapping" tag.
- Any request that does not get mapped to another resource will come down to our url mapping and will be handled by our dispatcher servlet.
- The Spring also needs a configuration file for dispatcher servlet.
- The file is called as "dispatcher-servlet.xml".
- This file is in WEB-INF directory.
- Add a new "Spring Bean Configuration File" in the directory "WEB-INF" and name it "dispatcher-servlet.xml".
- We need to ensure that Maven dependencies that we have included are there in "war" we will deploy.
- Open properties of the project from package-explorer.
- Select deployment assembly.
- Click add.
- Select java-build-path-entries.
- Select Maven dependencies.
- So we will have these dependencies in WEB-INF directory.
- Run the app and in console we will see Dispatcher Servlet with name "dispatcher" processing GET request.
- "web.xml" file
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee" xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_1.xsd" version="3.1">
<display-name>course-project</display-name>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
</beans>
- Now let us suppose we want to change the location of our dispatcher servlet.
- Let's create a new folder inside WEB-INF folder with name "spring".
- Move the dispatcher servelet to Spring folder.
- Run the application and we will get an error as
- "Could not open servlet context resource [/WEB-INF/dispatcher-servlet.xml]".
- To rectify this lets go back to our web.xml file and <init-param> to servlet tag inside this tag add
- <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
- <param-value>/WEB-INF/spring/dispatcher-servlet.xml</param-value>
- Close the </init-param> tag.
- Now app runs fine and XML bean definitions from Servlet Context resource will load.
- Inside <servlet-mapping>
- We can change <url-pattern>/springapp/*</url-pattern>
- This means all request which begin with "springapp" will be mapped to dispatcher servlet.
- We can have multiple configuration files lets add dispatcher2-servlet.xml to spring folder.
- We can load both these files using a wild card for value of "contextConfigLocation" parameter.
- The value is <param-value>/WEB-INF/spring/*-servlet.xml</param-value>.
- Now when we run we find "/WEB-INF/spring/*-servlet.xml" loads both the files.
- This wild card is mostly needed for loading root-application context to our configuration for Spring MVC.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee" xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_1.xsd" version="3.1">
<display-name>course-project</display-name>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/spring/*-servlet.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
Root Application Context
- Dispatcher Servlet creates a web application context.
- Root Application context contains all of our middle tier services like Data Access Services or Beans that handle our Business Logic.
- Root Application Context can be shared among multiple instances of a Dispatcher Servlet.
- We can Configure Spring JPA support and have two Dispatcher servlets that share those beans that perform Data persistence via Spring JPA.
- Configuring a Root Application Context involves following steps
- Create a listener in web.xml file.
- Inside Listener create a listener-class tag.
- The value would be "org.springframework.web.context.contextLoaderListener".
- This listener listens on the creation of our web application and the servlet context.
- It listens on different phases of the life-cycle of application i.e. when its initializing or its being destroyed on server.
- This listening is performed by observer methods that get called and queue these listeners to the different events within the life-cycle of the application.
- For example when we create the application the observer method in concern can build all of the application script objects or Beans.
- Once this "contextLoaderListener" is in place.It looks for a "xml configuration file" called as "applicationContext.xml".This file is searched in WEB-INF directory.
- "applicationContext.xml" is a file of type "spring bean configuration file".
- Any beans created in "applicationContext" file are available in xml configuration files for dispatcher servelets to use.
- Any bean can be referenced in "dispatcher-servelet.xml" file that is declared in our "applicationContext.xml" file.
- The reverse of this not true i.e. a bean declared in "dispatcher-servelet" and not available in "applicationContext.xml" file.
- If we run the application now we will see in our console that
- "XML bean definitions are loaded from servlet context resource "[/WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml]".
- To define a different location of the "application-context" file add a <context-param> tag after <listener> tag for contextLoaderListener.
- Inside this tag provide a tag "<param-name>" with value "contextConfigLocation".
- Next to this add "<param-value>" tag with value "/WEB-INF/spring/applicationContext,xml".
- "Root Application Context" is used to configure all the beans that are outside the scope of the "Dispatcher Servelet".
- "Dispatcher Servelet" performs all of the MVC Configuration and "Root Application Context" configure the beans not involved in MVC configuration such as "Data repository security" etc.
web.xml file
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee" xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_1.xsd" version="3.1">
<display-name>course-project</display-name>
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/spring/applicationContext.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/spring/*-servlet.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
applicationContext.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
</beans>
MVC Namespace
- Our MVC app needs configuration for dispatcher servlet.
- MVC Namespace provides these configurations.
- We use dispatcher-servlet.xml file to configure beans that are within our application-context that will control our request processing.
- Within the configuration file for our dispatcher we use mvc namespace.
- A namespace is a short tag used for a long snippet of xml.
- This long snippet controls the behaviour of our dispatcher servlet.
- In dispatcher-servlet.xml lets add 3 namespaces beans,context and mvc.
- Once we have selected the namespaces the *.xsd files of concerened namespaces are added to our xml file.
- Now we will use the "<mvc:annotation-driven/>" tag inside our dispatcher servlet.
- This tag configure beans that help us mapping request to controller methods using annotations.
- Supports data binding
- Supports custom validation.
- Custom converters that we use for data binding.
- Enables jsr 303 for validation support using annotations.
- Provides a conversion factory that provides us with predefined converters for common data types like date and number.
- Next we will create a controller class so that we can demonstrate the feature of mapping requests.
- We will create a new java class for this under the namespace "com.springimplant.mvc.controllers" with name "HomeController".
- Just above the class definition add the "@controller" annotation which makes this class a controller.
- Next we add a simple method called as "goHome" which will return a String "Welcome Home".
- Above this method we will add 2 more annotations
- "@RequestMapping("/home")"
- This maps this method to url request to the method
- "@ResponseBody"
- Make the string as body for our response
- Next we need to tell our IOC container associated with "dispatcher-servelet" to pickup our controller automatically.
- For this we will use the <context:component-scan base-package="com.springimplant.mvc.controllers"/>
- Run the project on server.
- Append "/home" to url and we will see the output on page "Welcome Home".
- Provides a mechanism to handle view resolution.
- Separates our controllers and models from views.
- We can change different views that interface with our model and controller.
- A view resolver is used to render the model into our browser
- This helps us to reduce dependency on a particular view always.
- When a view resolver is registered in Spring there is out of box support for jsp,patchy files,pdf and excel formats.
- Our controllers return a String which is either a name or a path to our views.
- In our controller file lets return the name of view "home" from the function we created called as "goHome()".
- This name represents one of our views that we have created and this can be handled by view resolver which can be used to create appropriate and correct view.
- Next we need to configure our view resolver we will do this in "dispatcher-servlet.xml".
- We will use an internal resource called as view resolver for this.
- It is used to handle our jsp files or mappings to our servlets
- Since these servlet's and jsp's are kept in in our WEB-INF directory we should not provide direct access to these.
- We should only use view resolver to access resources within our WEB-INF directory.
- Lets create a bean inside our dispatcher servlet with params
- id="viewResolver"
- class="org.springframework.web.servelet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver".
- In this bean there is a property for "prefix" and there is a property for "suffix".
- The value of "prefix" will be "/WEB-INF/views/".
- The value of suffix will be ".jsp" file.
- Now we are all set to access our view via controller we will hit the path defined in @RequestMapping("/home") and corresponding function will return the name of view "home" in this case.
- This name is appended by the prefix and suffix defined in view resolver which will provide its complete path.
- Lets run our program now and append "/home" to url to see results.
- Many times we need static resources such as files,images and js files used by our view from our "Webapp" directory.
- Lets first modify our jsp view file and add a text inside <h1> tag.
- We will change the color of this text to red.
- Lets add a "css file" inside webapp directory in a folder "/resources/css"
- Name it as "home.css" provide a style <h1> tag.
- Next we need to add a spring tag library into our ".jsp" so that we can provide our "css" file link.
- Add a declaration as <%@ taglib prefix="spring" uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags" />
- This declaration includes the tag library.
- It provides us with features like "data bindings","themes" and resolving urls.
- Inside the head tag add a tag <link rel="stylesheet" href="<spring:url value="/resources/css/home.css"/>" type="text/css" />
- This will include the css we just created.
- Note that the "spring:url" in link tag which adds url to the value.
- Run the project and add "/home" to the url.
- We will get an error that it cannot find our css because our every request is managed by the view resolver which is configured inside our dispatcher servlet.
- So since no controllers are mapped to the url we get a "page not found" error.
- Lets add "resources" tag inside our mvc namespace and configure it as follows.
- mvc:resource location="/resources/" mapping="/resources/**"
- We see we are using double astrix "**" in mapping.
- This is because we are using it in ANT style path mapping.
- This allows us to map urls that may have additional forward slashes.
- Run the project again and append "/home" to url and we will see it in red.
- We can check in webpage source that concerened css is correctly loaded this time.
package com.gaurav.mvc.controllers;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
@Controller
public class HomeController {
@RequestMapping("/home")
public String goHome()
{
return "home";
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd">
<mvc:annotation-driven/>
<context:component-scan base-package="com.springimplant.mvc.controllers"/>
<bean id="viewResolver" class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/views/"></property>
<property name="suffix" value=".jsp"></property>
</bean>
<mvc:resources location="/resources/" mapping="/resources/**"></mvc:resources>
</beans>
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1"
pageEncoding="ISO-8859-1"%>
<%@ taglib prefix="spring" uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags" %>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1">
<title>Insert title here</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="<spring:url value="/resources/css/home.css"/>" type="text/css"/>
</head>
<body>
<h1>This page is called using a view resolver</h1>
</body>
</html>


No comments:
Post a Comment